Understanding the debt to equity ratio is essential for anyone dealing with finances, whether you’re an investor, a financial analyst, or a business owner. It shines a light on a company’s financial structure, revealing the balance between debt and equity. It’s not just about numbers; it’s about understanding the story behind those numbers. On the other hand, companies with low debt-to-equity ratios aren’t always a safe bet, either. For example, a company may not borrow any funds to support business operations, not because it doesn’t need to but because it doesn’t have enough capital to repay it promptly. Changes in long-term debt and assets tend to affect the D/E ratio the most because the numbers involved tend to be larger than for short-term debt and short-term assets.
Effect of Debt-to-Equity Ratio on Stock Price
The D/E ratio is much more meaningful when examined in context alongside other factors. Therefore, the overarching limitation is that ratio is not a one-and-done metric. The following D/E ratio calculation is for Restoration Hardware (RH) and is based on its 10-K filing for the financial year ending on January 29, 2022. Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others.
Underlying Concept of Debt to Equity Ratio
When an investor decides to invest in a company, she needs to know the company’s approach. Businesses often experience decreased revenue during recessions, making it harder to fulfill debt obligations and thus raising the D/E ratio. Those that already have high D/E ratios are the most vulnerable to economic downturns.
What is debt-to-equity ratio?
For this reason, it’s important to understand the norms for the industries you’re looking to invest in, and, as above, dig into the larger context when assessing the D/E ratio. Airlines, as well as oil and gas refinement companies, are also capital-intensive and also usually have high D/E ratios. One limitation of the D/E ratio is that the number does not provide a definitive assessment of a company.
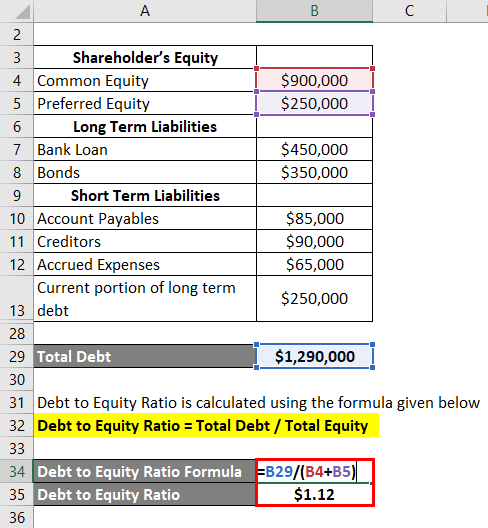
If the D/E ratio of a company is negative, it means the liabilities are greater than the assets. These can include industry averages, the S&P 500 average, or the D/E ratio of a competitor. You can calculate the D/E ratio of any publicly traded company by using just two numbers, which are located on the business’s 10-K filing. However, it’s important to look at the larger picture to understand what this number means for the business. Below is an overview of the debt-to-equity ratio, including how to calculate and use it. 11 Financial may only transact business in those states in which it is registered, or qualifies for an exemption or exclusion from registration requirements.
Role of Debt-to-Equity Ratio in Company Profitability
- Not all debt is considered equally risky, however, and investors may want to consider a company’s long-term versus short-term liabilities.
- This ratio helps indicate whether a company has the ability to make interest payments on its debt, dividing earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) by total interest.
- This is also true for an individual applying for a small business loan or a line of credit.
- The debt-to-equity ratio (aka the debt-equity ratio) is a metric used to evaluate a company’s financial leverage by comparing total debt to total shareholder’s equity.
- What counts as a good debt ratio will depend on the nature of the business and its industry.
- The long-term D/E ratio for Company A would be 0.8 vs. 0.6 for company B, indicating a higher risk level.
Gearing ratios constitute a broad category of financial ratios, of which the D/E ratio is the best known. While a good debt-to-equity ratio for your personal finances would ideally remain below 1.0, many homeowners hold more debt than equity in their homes. If your debt-to-equity ratio is high because of your home, aim to keep debt from other sources low. We can easily calculate good debt to equity ratio ratio in the template provided. All we need to do is find out the total liabilities and the total shareholders’ equity. It gives a fast overview of how much debt a firm has in comparison to all of its assets.
If earnings outstrip the cost of the debt, which includes interest payments, a company’s shareholders can benefit and stock prices may go up. Using excel or another spreadsheet to calculate the D/E is relatively straightforward. First, using the company balance sheet, pull the total debt amount and the total shareholder equity amount, and enter these numbers into adjacent cells (e.g. E2 and E3).

In the consumer lending and mortgage business, two common debt ratios used to assess a borrower’s ability to repay a loan or mortgage are the gross debt service ratio and the total debt service ratio. It’s great to compare see top 10 analytics and business intelligence trends for 2021 debt ratios across companies; however, capital intensity and debt needs vary widely across sectors. The financial health of a firm may not be accurately represented by comparing debt ratios across industries.
In most cases, this would be considered a sign of high risk and an incentive to seek bankruptcy protection. We can see below that for Q1 2024, ending Dec. 30, 2023, Apple had total liabilities of $279 billion and total shareholders’ equity of $74 billion. In 2021, commercial real estate company Washington Prime Group (WPG) declared bankruptcy after the pandemic forced many of WPG’s tenants to close down, leaving the company with a huge decline in revenue.
Looking at the balance sheet for the 2023 fiscal year, Apple had total liabilities of $290 billion and total shareholders’ equity of $62 billion. However, that’s not foolproof when determining a company’s financial health. Some industries, like the banking and financial services sector, have relatively high D/E ratios and that doesn’t mean the companies are in financial distress.
Recent Comments